As emissions regulations tighten and environmental awareness grows, vehicle components playing central emissions control roles have become spotlighted. In particular, the exhaust gas recirculation / EGR valve has emerged as a critical player within vehicle air quality management ecosystems.
EGR valves enable controlled redirection of exhausted gases back into intake systems. This exhaust gas recirculation mechanism strategically lowers resulting combustion temperatures to reduce nitrous oxide and particulate matter formation.
With tailpipe outflow serving as the primary pollution outlet of internal combustion engines, effectively treating emissions via EGR optimization helps engine designers balance power targets and emissions constraints.
While EGR valves focus mainly on reducing exhaust byproduct formation rates, catalytic converters treat existing noxious compounds through precious metal chemical conversion triggering.
Their combined placement converts and partly reuses waste gases to limit environmental release volumes, meeting regulatory compliances. When either component underperforms, vehicle emissions responsibilities grow compromised.
This crucial interaction and emissions purpose necessitates proper EGR education for mechanics and owners seeking holistic vehicle health insights with an environmental eye conscientiously focused forward.
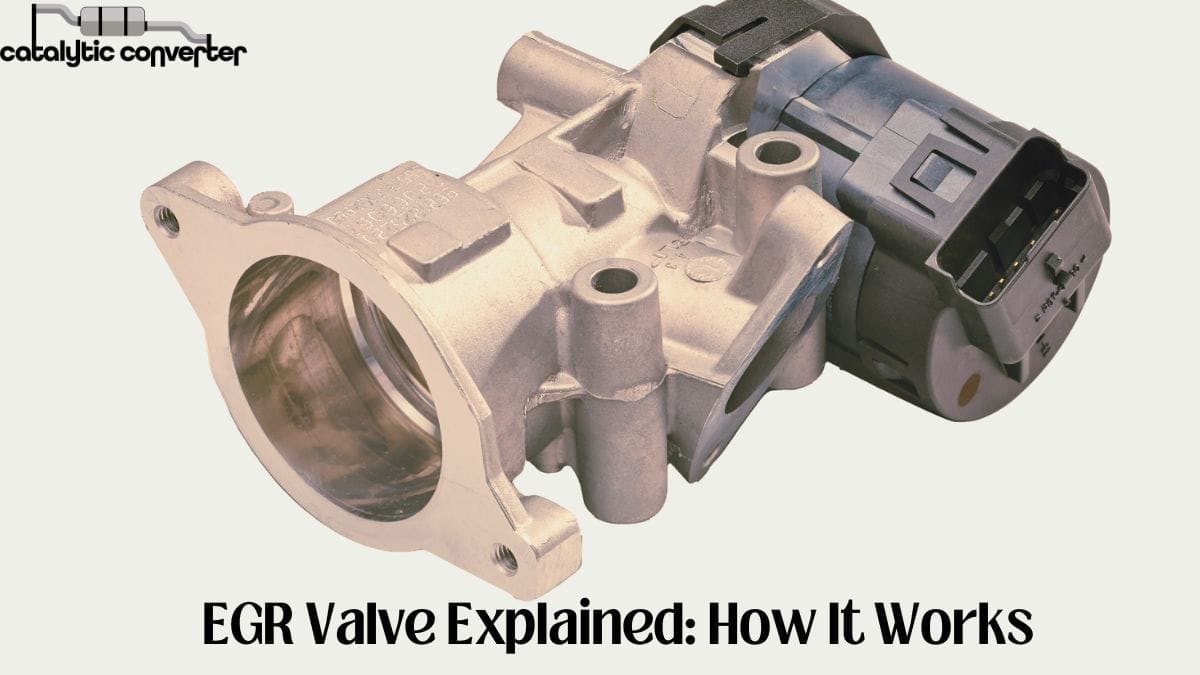
What is an EGR Valve and How Does it Work?
An EGR valve is an emissions device that reverts motor exhaust into the combustion chambers.
It works by opening at specific times during the engine cycle to route cooled fumes from the exhaust manifold into the intake manifold, mixing with fresh oxygen-rich air.
Want to learn more about how to upgrade your car’s exhaust system? Check out our guide on The Exhaust System Components and Upgrades.
Sensor feedback calibrates valve opening rates to limit oxygen content, thus lowering resulting combustion temperatures and reducing nitrous oxide formation rates.
The Purpose and Function of the EGR Valve
The main EGR valve purpose includes:
Lower Peak Combustion Temperatures
Reducing oxygen content lowers temperatures, mitigating NOx creation, which spikes sharply above 2500°F.
Increase Exhaust Gas Volumetric Efficiency
Reusing waste exhaust gases instead of expelling them entirely improves consumption efficiency and fuel mileage.
Improved Engine Efficiency
Cooler intake charge densities improve combustion efficiency. Recirculation lowers pumping losses.
Meet Emissions Regulations
Lower particulate and NOx emissions align with modern compliance standards.
When appropriately calibrated with ideal choking rates across operating ranges, noticeable fuel economy gains also accrue partly from recycling exhaust gases.
Symptoms of a Bad EGR Valve
Common failure symptoms include:
Check Engine Light
Controller fault codes flag EGR sensor issues or flow duty cycle deviations.
Poor Engine Performance
Uneven running from incorrect air/fuel ratios. Loss of power and throttle response from reduced vacuum.
Failed Emission Testing
Uncontrolled NOx release exceeding limits fails regulatory compliance.
Lower Fuel Mileage
Incorrect choking causes running rich and wasting fuel—higher pumping losses sap efficiency.
Catching issues early prevents damage across interconnected intake components and restores intended engine performance optimization targets.
EGR Valve Replacement and Maintenance
Most EGR valves are highly durable, lasting over 100k miles with minor maintenance like intermittent cleaning. However, higher contaminant oil blowby and sooty diesel intake deposits accelerate wearing. Monitor for flaky deposits around valve stems indicating flow issues.
Replacement costs typically run $150-$250 for parts and labor. DIY options under $90 exist but require expert mechanical skills. Refurbished/remanufactured units offer lower-cost alternatives to new ones.
Different Types of EGR Valves
Electronic EGR Valves feature precise computer-controlled stepper motors with closed-loop operation monitoring. This improves flow tuning accuracy over purely vacuum-actuated designs.
Positive Backpressure EGR Valves induce intentional exhaust restrictions via flow orifice plates to drive higher manifold pressures for boosted recirculation rates. Useful in naturally aspirated engines.
Negative Backpressure EGR Valves use intake throttling to produce vacuum flow suction through unfettered exhaust return channels. No exhaust flow blocking makes them more robust.
Cooler Bypass EGR Valves allow temperature regulation of redirected exhaust gases before downstream charge air cooler delivery through selective routing modulation. This prevents overchilling.
History and Evolution of EGR Valve Technology
The first EGR systems debuted in the 1960s using crude mechanical linkage designs before the widespread adoption of precision stepper motor electronic valve actuation integrated with engine computer monitoring for accurately optimized exhaust gas recalculation functionality.
Expect continued innovation as automakers experiment with emerging expander cycle EGR approaches harnessing waste heat into useable mechanical energy recaptured through specialty turbines or piston linkages, partially offsetting pumping losses. Recycling efficiencies continue progressing.
EGR Valves and Exhaust Systems
Examining the tight integration of EGR valves within the broader exhaust ecosystem reveals their paramount role in balancing engine performance against environmental responsibilities.
The Vital EGR and Exhaust System Relationship
While catalyst-equipped mufflers focus mainly on cleaning already expelled gases, EGR valves serve higher upstream, limiting harmful byproduct generation rates through below-threshold temperature maintenance.
This smarter emissions reduction approach decreases the required catalyzer load through preemptive avoidance. Only optimally paired EGR heat-choked flow rates balance engine needs against eco-impact.
Connecting Catalytic Converters and EGR Function
EGR ratios exceeding ideal thresholds overload catalytic systems with excess hydrocarbon and particulate matter flows beyond maximum conversion capacity, damaging cells through overloaded chemical reaction cascading and mechanical clogging.
This resulted in post-catalysis excess emissions, then defeated initial EGR prevention attempts through misbalanced integration between intake flow interventions and exhaust treatment workload capacities.
If you’re curious about cars and want to learn more about how they work, you might be interested in discovering what a catalytic converter is and how it operates.
Ideally, calibrated EGR rates ensure catalytic bricks stay within peak operation zones without quenching or overloading failure modes kicking in. This harmony enables reduced eco-impact in unison rather than through isolated mechanisms lacking cohesive system perspectives.
The Emissions Control Role of EGR Valves
EPA emissions studies on heavy-duty diesel truck applications indicate optimized EGR usage decreases particulate matter by 50-90% while nitrous oxides drop 35%. Gasoline vehicle NOx emissions saw 20-50% reductions.
Their substantial impact on lowering air quality hazards rightly classifies properly functioning EGR valves as vital emissions control participants – especially as catalyst materials age, degrading containment assurance.
Troubleshooting EGR Valve Issues
Identifying issues early and optimizing integrations with complementary technologies prevents power losses from snowballing drivability and environmental compliance consequences.
Catching small initial driving changes promptly diagnoses underlying issues before additional intake component fouling further masks emerging root causes.
How to Test Your EGR Valve
Common DIY diagnostic steps include:
1. Visual Inspection – Check for loose connections, damage, or corrosion
2. Resistance Testing – Use a multimeter to measure solenoid winding resistance
3. Vacuum Testing – Ensure the valve opens under vacuum delivery during idle
4. Voltage Testing – Check for clean power signal delivery to stepper motor
5. Exhaust Backpressure Test – Measure variations between idle and accelerated states
Isolating failures requires methodically eliminating each potential root cause through structured troubleshooting sequences before pricey parts replacements.
- Tools and Steps for Diagnosing EGR Issues
- Connect scan tool checking for P0401 insufficient flow codes
- Perform visual inspections of electrical harnessing
- Use graphs to log real-time position sensor feedback for stability
- Check actuating diaphragm welds for cracking failure
- Measure inlet and outlet port backpressures across operating states
Service manuals detailing emissions testing procedures prove invaluable for smoothly navigating complex diagnostic sequencing, especially for identifying intermediate default modes.
EGR Valve Fault Codes
P0400 – Insufficient EGR flow detected
P1406 – EGR valve position sensor issues
P0404 – EGR open/closed performance failure
P0403 – Excessive EGR flow detected
Isolating the specific fault code avoids misguided component replacements, correcting only outward symptoms, not inner root causes. Develop fixes addressing total systemic implications through DFA analysis.
Common Causes of EGR Valve Failure
Carbon Buildup – Sticky deposits impede flow
Stuck Pintles – Fouling debris jams, moving valve flaps
Vacuum Leaks – Insufficient actuator pressure from disconnected lines
Electrical Shorts – Burnt-out solenoid windings prevent position regulation
Coolant Leaks – Loss of heat exchanging liquids impairs temp controls
Exhaust Leaks – External manifold cracks bypass the intended choked flow
Meticulous build quality and preventative maintenance vastly improve longevity prospects through contaminant reductions and leakage protections.
EGR Valve Cleaning and Maintenance
Keeping EGR pathway elements clear of obstructing deposits maintains intended functionality.
- DIY EGR Cleaning Step-by-Step:
- Remove electrical connector
- Unbolt the valve from the intake
- Clean the pintle with carb cleaner, spraying down stems
- Brush chamber walls and port holes
- Flush all passages with pressurized water
- Verify smooth manual valve motion
- Use brake cleaner spray on electrical moving contact points
- Reinstall the valve with new gaskets
Repeat cleaning every 60k miles or during major tune-ups. Upgrade to stainless steel valves and gasket-sealed connectors in colder winter climates.
Recommended EGR Cleaning Techniques
Ultrasonic Cleaning bombards stuck on carbon layers with soundwave cavitations disintegrating deposits. Provides deep internal passageway restorations.
Media Blasting uses walnut shell grain, baking soda, or glass beads to gently strip caked soot without the metal-damaging risks of sandblasting approaches.
Both methods are superior to DIY soaking or surface spraying methods, which cannot address hidden internal buildups, eventually impeding flow rates. Consider professional shop cleaning services for thorough contaminant removal – especially on older vehicles.
EGR Valve Maintenance Tips
- Use fuel injector cleaners to prevent intake value clogging from fuel residue.
- Fix oil leaks immediately, preventing fouling carbon accumulation
- Select high-detergent motor oils to suspend contaminants
- Check for stuck open valves causing poor idling and stalling
- Confirm EGR gasket sealing integrity during smoke visual inspections
Proper ongoing maintenance better sustains engineered emissions reduction performance and fuel economy through sustained intelligently controlled exhaust gas recirculation functionality.
EGR Valve Variances Across Vehicle Types
While EGR principles stay rooted in expenditure stream recycling and combustion temperature reduction strategies, notable calibration variances manifest among diesel and gasoline engine architectures.
EGR Valves in Gasoline Engines
Conventional port fuel injected (PFI) gasoline EGR systems feature external cooling to prevent pre-detonation risks from hot redirected exhaust exceeding thermal limits of air/fuel charge mixtures. This sustains peak volumetric intake flow efficiency.
Modern gasoline direct injection (GDI) applications skip dedicated EGR coolers thanks to injected liquid fuel layers protecting chamber surfaces from residual exhaust heat. This, however, stresses injection systems with higher soot contamination risks requiring low-sulfur fuels.
EGR Valves in Diesel Applications
Unlike gasoline engines risking performance-sapping pre-ignition from hot EGR gases, diesels conversely rely on sufficiently heated recycled exhaust to maintain efficient cylinder heat levels for clean combusting.
EGR alone often fails to reduce particulate matter formations, especially under higher loads, without further assistance from diesel particulate filters (DPF). Systems work cohesively, balancing workloads for improved longevity.
Gasoline vs Diesel EGR Distinctions
| Gasoline EGR | Diesel EGR | |
|---|---|---|
| Temp | Cooled | Hot |
| Goal | Lower NOx | Reduce Soot |
| Load | Mainly Partial Load | High Load Usage |
| Supplements | Catalytic Converters | DPF Particulate Filters |
Striving for balanced integration recommendations tailored across engine architectures based on manufacturer telemetry analytics of each subcomponent’s purpose relative to connected dependencies better promotes collectively optimized vehicle health.
EGR Valves in Specific Engine Models
Notable EGR distinctions exist across various engine models from differing OEMs worth highlighting for mechanics servicing affected vehicles:
Cummins EGR Systems
Top Cummins engines, including the revered 5.9-liter 12-valve and 24-valve 6.7-liter units, feature smart electronic EGR valves offering typical exhaust redirection abilities and exhaust manifold flow modulation abilities for finer air/fuel ratio controls.
This dual-acting functionality allows downstream sensor feedback optimization of both intake oxygen density via variable exhaust restrictions alongside calibrated EGR mixing ratios, advancing responsible power and emissions synergies through consolidated actuation integration.
Ford Powerstroke EGR Details
Across Super Duty diesel models, Ford has continually refined EGR positioning strategies culminating in dual upstream/downstream valve placements, enabling cold start emissions improvements and cruising particulate reductions combining calibration strengths from two different temperature profile vantage points.
Styl steel exhaust manifolds and EGR coolers also resist corrosion damage from condensed water mixing with hot exhaust gases – a common Powerstroke issue as engines age.
GM Duramax Systems
Duramax engines, in their heavy-duty truck applications since 2011, integrate dedicated EGR engine coolant heat exchangers into cylinder heads, achieving rapid flow warming through jacketing integration vs slower underbody ambient air passing approaches.
This enables faster optimal operating temperatures for the EGR cycle to initiate emissions containment work, especially during shorter trips lacking extended steady-state operating durations.
EGR Valve Replacement and Upgrades
When functionality becomes compromised, properly recalibrating or replacing EGR valves restores emissions compliance.
EGR Valve Replacement Costs
Parts: $100 – $300
Labor: 1-3 hours
Total: Approximately $300 to $600
Slight variances exist between easy-to-access top-mounted configurations vs. hard-to-reach externally positioned units requiring significant intake dismantling – so factor accessibility into quotes.
- DIY EGR Valve Replacement
- Disconnect electrical connector
- Unbolt the EGR valve from the exhaust/intake
- Remove intake components if the valve is located internally
- Scrape old gasket material away
- Install new valve with fresh gaskets
- Reattach hoses and electrical plug
- Clear fault codes and test drive vehicle
Those inexperienced with handling pressurized coolant hoses or electrical sensors may prefer leaving complex internal access installations to professional mechanics better positioned to navigate intricacies smoothly.
Upgraded EGR Valve Options
Socketed Pintles – Reduce fouling stickiness and calibration inconsistencies
Stainless Housings – Resist corrosion from condensation and oil leaks
Ceramic Internals – Withstand higher exhaust heat and carbon buildup
Ported Shrouds – Retain hot EGR exhaust gases for diesel engine compatibility
Teflon Seals – Prevent vacuum leaks around valve stems
Aftermarket upgrades provide tuned durability and heat protection for sustaining precision control authority over all operating regimes, incredibly abusive towing applications, or extreme cold weather reliability demands.
EGR Valves Environmental Impact
The emissions containment abilities directly demonstrated through mandated OBD-II monitoring play a measurable role in limiting transportation impact.
EGR Valves Significantly Reduce Vehicle Emissions
Alongside advanced fuel injection governance strategies and catalyzers after treatment conversions – calibrated EGR ratios lowering cylinder temperatures and using waste gases efficiently comprise the essential third leg of managing environmental overreach restraint through internal negation rather than merely slow external treatments unable to keep pace with modern powerplant outputs.
EPA trucking studies showed properly operating EGR functionality cutting diesel particulate emissions over 90% while continuing to curb nitrous oxide generation – preventing tons of contamination annually as transport mileages continue expanding.
Global Emissions Regulations Increasingly Strict
As climate goals tighten amidst warming atmospheric carbon levels and public health concerns from pollution, emissions mandates have grown understandably strict, often pushing engineering boundaries for combustion byproduct containment capabilities before widespread electrification localization sufficiently progresses.
EGR innovations are key to sustaining internal combustion relevancy as regulatory allowances narrow through deep thermal dynamic transformations and rare exhaust filtration. Efficiency refinements stretch precious fossil fuel energy density, concentrating useable work potential before absolute depletion.
Public Health Impact of EGR Emissions Control
Studies analyzing air quality in notorious smog-afflicted traffic urban areas have connected earlier introduction of EGR systems with marked reductions in measurable nitrous and particulate levels – providing direct health benefits by reducing respiratory issues and cardiovascular complications from exposure-triggered inflammations.
Curbing transportation-rooted emissions sources proactively protects vulnerable populations unable or unwilling to pick up stakes and retreat from contaminated environments unsustainably shared under previous peak urban density mobility ignorance. Our narrowing emissions allowances rightly force accountability.
EGR Valves and Engine Performance
Effects of a Malfunctioning EGR Valve on Engine Performance and Efficiency
When an EGR valve malfunctions, its impact on engine performance and efficiency becomes apparent. The most immediate effect is a disruption in the air-fuel mixture, leading to uneven combustion. This can result in poor acceleration, reduced torque, and decreased power output.
Additionally, a malfunctioning EGR valve may cause increased fuel consumption, compromising the vehicle’s efficiency. Understanding these effects is crucial for promptly identifying and resolving EGR valve issues to maintain optimal engine performance.
Improving Engine Performance with EGR Valve Tuning
EGR valve tuning offers a potential avenue for enhancing engine performance. By calibrating the opening and closing rates of the EGR valve, it becomes possible to fine-tune the combustion process.
This tuning can improve throttle response, smoother running, and optimized power delivery. However, it’s essential to strike the right balance to avoid adverse effects, making EGR valve tuning a specialized skill requiring engine dynamics and emissions control expertise.
EGR Valve Performance Tuning: What You Should Know
Delving into the nuances of EGR valve performance tuning, it’s crucial to understand the intricacies involved. Proper tuning involves adjusting the valve’s behavior to optimize combustion temperatures, reduce NOx emissions, and enhance fuel efficiency.
This process often requires specialized tools and knowledge of the vehicle’s engine management system. While EGR valve tuning can yield positive results, it should be approached cautiously, as improper adjustments may lead to unintended consequences, affecting engine performance and emissions.
The Relationship Between EGR Valves and Engine Power
The relationship between EGR valves and engine power is intricate, with the valve’s role extending beyond emissions control. While the primary purpose is to reduce NOx emissions, the EGR system’s influence on peak combustion temperatures can impact engine power.
Striking the right balance is crucial; excessive EGR rates can lead to reduced power due to lower combustion temperatures, while inadequate rates may result in increased emissions. Understanding this delicate relationship is essential for optimizing both power and emissions in internal combustion engines.
Fuel Economy and EGR Valves: Finding the Right Balance
The impact of EGR valves on fuel economy is a critical consideration for vehicle owners and manufacturers alike. When properly calibrated and functioning, EGR valves contribute to improved fuel efficiency by recycling exhaust gases and reducing pumping losses.
However, finding the right balance is crucial, as overly aggressive EGR usage may lead to incomplete combustion and decreased fuel economy. Striking the optimal balance between emissions control and fuel efficiency is key to managing vehicle operation’s environmental and economic aspects.
EGR Valves and Other Vehicle Systems
EGR Valves and Their Impact on the Exhaust Gas Recirculation System
Understanding how EGR valves interact with the broader exhaust gas recirculation system is vital for comprehending their overall impact. The EGR system, consisting of valves, coolers, and associated components, collaborates to manage emissions and maintain engine efficiency.
A malfunctioning EGR valve can disrupt this system, leading to increased emissions and potential damage to other components. Proper understanding and maintenance of the entire EGR system are crucial for sustained vehicle performance.
Understanding the Interaction Between EGR Valves and the Turbocharger
The relationship between EGR valves and turbochargers plays a significant role in engine efficiency. EGR valves influence exhaust gas flow, which, in turn, affects the turbocharger’s performance.
A well-calibrated EGR system can contribute to optimal turbocharger operation, enhancing engine efficiency. However, improper EGR function or excessive rates may impact the turbocharger negatively, leading to decreased performance and potential long-term damage.
Engine Oil and EGR Valves: Effects and Maintenance Tips
The connection between engine oil and EGR valves is often overlooked but holds importance for overall engine health. EGR valves can introduce contaminants into the engine oil, leading to accelerated wear and reduced lubrication efficiency.
Regular oil changes and monitoring oil quality are essential maintenance practices to mitigate these effects. Additionally, selecting high-quality oils that resist breakdown in the presence of EGR-related contaminants is crucial for maintaining engine longevity.
EGR Valves and Their Role in the Air Intake System
EGR valves play a pivotal role in the air intake system by regulating the flow of recirculated exhaust gases into the combustion chambers. This interaction affects the composition of the air-fuel mixture, combustion temperatures, and, consequently, engine performance. Understanding how EGR valves integrate into the air intake system is fundamental for diagnosing airflow, combustion, and emissions issues.
EGR Valves and the Cooling System: How They Are Connected
The relationship between EGR valves and the cooling system is crucial for managing engine temperatures. EGR systems often include coolers to lower the temperature of recirculated exhaust gases before reintroduction into the combustion chambers.
Proper functioning of EGR coolers is essential for preventing overheating and maintaining optimal engine performance. Regular cooling system inspection and maintenance, including EGR coolers, improve vehicle reliability.
FAQs Related to Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve
What Is an EGR Valve?
An EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) valve is a component in a vehicle’s engine system that recirculates a portion of exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber.
What Is the Purpose of the EGR Valve?
The EGR valve helps reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by lowering combustion temperatures and preventing the formation of harmful pollutants.
What Does an EGR Valve Do?
The valve opens and allows a controlled amount of exhaust gas to enter the intake manifold, mixing with fresh air and reducing the oxygen content during combustion.
Can a Faulty EGR System Affect Engine Performance?
A malfunctioning EGR valve can lead to poor engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and higher emissions.
What Are Common Signs of a Failing EGR Valve?
Symptoms include rough idling, engine knocking, reduced fuel efficiency, and the illumination of the check engine light.
How Often Should the EGR Valve Be Replaced or Cleaned?
The replacement interval varies, but it’s advisable to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and address issues promptly.
How Does the EGR Valve Interact with the Exhaust System?
The EGR valve is a crucial component that connects the exhaust system to the engine intake, facilitating the recirculation of exhaust gases.
Can Issues with the Exhaust System Affect EGR Valve Performance?
Yes, problems such as leaks or restrictions in the exhaust system can impact the proper functioning of the EGR valve.
Do Exhaust System Repairs Require EGR Valve Inspection?
While not always necessary, inspecting the EGR valve if extensive exhaust system repairs are undertaken is advisable.
Can a Damaged Catalytic Converter Affect the EGR Valve?
In some cases, a failing catalytic converter may contribute to issues with the EGR valve, as both components play roles in emission control.
How Are the EGR Valve and Catalytic Converter Related?
Both components contribute to emissions control, with the EGR valve reducing NOx emissions and the catalytic converter converting harmful pollutants.
Do Catalytic Converter Problems Affect the EGR Valve?
While not directly connected, extensive issues with the catalytic converter can contribute to overall emission control system malfunctions, indirectly affecting the EGR valve.
Are There Any Maintenance Tips for the Health of the EGR Valve and Catalytic Converter?
Regular inspections, prompt addressing of issues, and adherence to manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules contribute to the health of the EGR valve and catalytic converter.
Where is the Location of the EGR Valve on The Engine?
The EGR valve is typically on or near the engine’s intake manifold.
Conclusion on Exhaust Gas Recirculation System
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of EGR valves involves recognizing their key components and functions. Each element plays a vital role in emissions control and engine efficiency, From the valve to associated systems like coolers and the exhaust gas recirculation system.
Recapitulating these key components ensures a holistic perspective on the importance of EGR valves in maintaining a balance between environmental responsibility and optimal vehicle performance.
Emphasizing the importance of regular maintenance cannot be overstated regarding EGR valves. Routine checks, timely cleaning, and adherence to recommended service intervals contribute to optimal EGR valve performance.
Regular maintenance ensures emissions compliance and enhances engine efficiency, prolongs component lifespan, and minimizes the risk of costly repairs. Prioritizing regular maintenance practices is a proactive approach to preserving the health and performance of a vehicle’s EGR system and, by extension, the entire internal combustion engine.